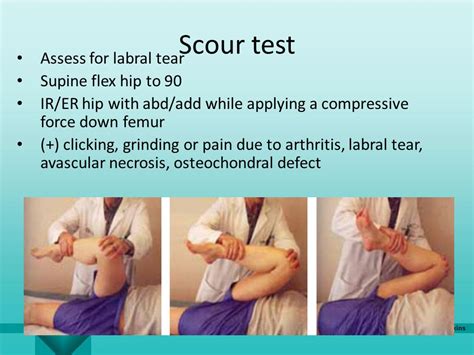
labral tear hip special tests|labral tear physical exam tests : factory Step 1:The patient should be lying supine with their head supported and both arms rested to their side in a comfortable position. Step 2:The . See more The instructions will tell you exactly where and how to load the items you're trying to sterilize. Make sure instruments undergone cleaning and disinfection, prior to sterilization.
{plog:ftitle_list}
The autoclave applies high pressure (15 psi) and saturated steam at 121oC (250oF) for 15-20 minutes to kill microbes and spores. After the media has gone through this cycle, it is sterile. Cool to 60-65oC before .Standard operating procedure of cleaning of SAS air sampler used for detectinion of microbial contamination in air.
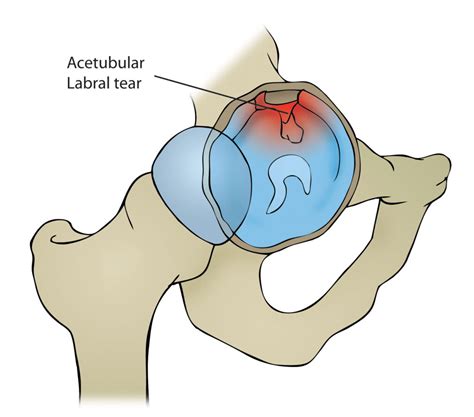
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. See more
The acetabulofemoral (hip) joint is the largest and most stable joint in the human body. The acetabular labrum is a soft-tissue structure . See moreStep 1:The patient should be lying supine with their head supported and both arms rested to their side in a comfortable position. Step 2:The . See moreTo test for an anterior labral tear, the patient lies supine, then the physical therapist (PT) .
Hip special tests are useful for identifying hip pathology such as labral tears, muscular injuries, hip and low back pathology, and other conditions. Below you will find a list of hip special tests and links to each test with description and video if available.The log roll test is used to assess the integrity of the hip joint and is used to help identify potential hip pathology such as labral tears, ligament laxity, or impingement.Shoulder special tests are useful for identifying shoulder pathology such as rotator cuff tears, impingement, instability, biceps injury, and labral tears. Below you will find a list of shoulder special tests and links to each test with description and video if available.The Trendelenburg test is useful for identifying weakness or instability of the lateral hip musculature, specifically gluteus medius weakness or pathology. Position of Patient: The patient should be standing with feet shoulder width apart.
The FABER test is used to identify the presence of sacroiliac joint dysfunction or SI joint dysfunction. It’s one of the most commonly used provocation tests of the hip. Position of Patient: The patient should be relaxed in the supine position as the examiner flexes the patient’s knee to 90 degrees, resting their foot on their opposite knee.The Biceps Load 2 test is used to identify labral tears (SLAP Lesions) Position of Patient: Position the patient in supine. Performance: The examiner will grasp the patient’s wrist and elbow and elevate the arm to 120 degrees of abduction and elbow at 90 degrees of flexion. Fully rotate the arm into external rotation and forearm supination.There are many special tests clinicians can use to diagnose orthopedic and other musculoskeletal impairments. The orthopedic tests listed on this page are designed as a quick reference based on region and further classified into special test based on impairment if indicated.
The Apprehension test is used to help identify shoulder instability and is considered one of the best tests for identifying this pathology. Position of Patient: Patient is sitting or standing with .The Speed’s test is used to assess the integrity of the biceps tendon (long head) or labrum, specifically a Superior Labrum Anterior-Posterior (SLAP) Lesion. Performance: The examiner will apply a downward force to the patient’s arm at the 90 degree position.The Yergason’s test is used to identify tears in the glenoid labrum, as well as biceps pathology. Have the patient positioned in sitting or standing with elbow at 90 degrees of flexion.Hip special tests are useful for identifying hip pathology such as labral tears, muscular injuries, hip and low back pathology, and other conditions. Below you will find a list of hip special tests and links to each test with description and video if available.
The log roll test is used to assess the integrity of the hip joint and is used to help identify potential hip pathology such as labral tears, ligament laxity, or impingement.
Shoulder special tests are useful for identifying shoulder pathology such as rotator cuff tears, impingement, instability, biceps injury, and labral tears. Below you will find a list of shoulder special tests and links to each test with description and video if available.The Trendelenburg test is useful for identifying weakness or instability of the lateral hip musculature, specifically gluteus medius weakness or pathology. Position of Patient: The patient should be standing with feet shoulder width apart.The FABER test is used to identify the presence of sacroiliac joint dysfunction or SI joint dysfunction. It’s one of the most commonly used provocation tests of the hip. Position of Patient: The patient should be relaxed in the supine position as the examiner flexes the patient’s knee to 90 degrees, resting their foot on their opposite knee.
labral tear physical exam tests
The Biceps Load 2 test is used to identify labral tears (SLAP Lesions) Position of Patient: Position the patient in supine. Performance: The examiner will grasp the patient’s wrist and elbow and elevate the arm to 120 degrees of abduction and elbow at 90 degrees of flexion. Fully rotate the arm into external rotation and forearm supination.There are many special tests clinicians can use to diagnose orthopedic and other musculoskeletal impairments. The orthopedic tests listed on this page are designed as a quick reference based on region and further classified into special test based on impairment if indicated.
The Apprehension test is used to help identify shoulder instability and is considered one of the best tests for identifying this pathology. Position of Patient: Patient is sitting or standing with .
The Speed’s test is used to assess the integrity of the biceps tendon (long head) or labrum, specifically a Superior Labrum Anterior-Posterior (SLAP) Lesion. Performance: The examiner will apply a downward force to the patient’s arm at the 90 degree position.
how can one heal a hip labral tear
how to use refractometer for gemstones
how to use refractometer for glycol
hip labrum physical exam test
A Sterilization Autoclave is a Pressure Vessel intended to perform a Sterilization Process, i.e., the complete inactivation of all viable micro-organisms inside pharmaceutical products for human .
labral tear hip special tests|labral tear physical exam tests